COMPUTER GUIDED IMPLANT SURGERY
Computer-guided implant surgery, also known as computer-assisted implant surgery or guided implant surgery, is an advanced approach that incorporates digital technology, including 3D imaging and CAD/CAM software, to plan and execute dental implant procedures.
Computer-guided implant surgery enhances the predictability, precision, and safety of dental implant procedures, allowing for minimally invasive and efficient treatment. It is particularly beneficial for complex cases, ensuring that the patient receives optimal results with minimal discomfort and downtime.
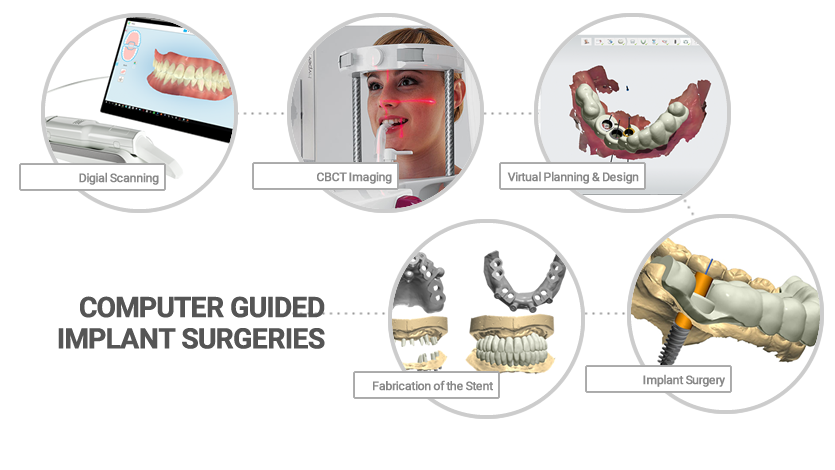
STEPS TO COMPUTER GUIDED IMPLANT SURGERY
| Placement of dental implants is a complex dental procedure that involves several steps. It’s important to note that dental implant procedures should only be performed by trained and experienced dental professionals. Here are the general steps involved in the placement of dental implants: |
|---|
- Comprehensive Examination: The dentist will perform a thorough examination of your oral health, including X-rays, scans, and possibly a 3D CT scan. This helps in assessing the bone quality, quantity, and location for implant placement.
- Treatment Plan: Based on the examination, the dentist will create a customized treatment plan. This plan considers factors like the number and location of implants needed, the type of restoration (crown, bridge, denture), and any additional procedures required (bone grafting, sinus lift, etc.).
- Specialized software is used to create a virtual treatment plan, which includes selecting the ideal implant positions, angulations, and depths.
- Based on the virtual treatment plan, a surgical stent is digitally designed to guide the implant placement accurately.
- The digital design of the stent is then used to create a physical stent through 3D printing or other fabrication methods.
- During the surgery, the stent is placed over the patient’s teeth and gums, serving as a guide for the dentist to precisely place the implants.
- The stent ensures that the implants are inserted exactly where planned, leading to improved outcomes and reduced margin for error.
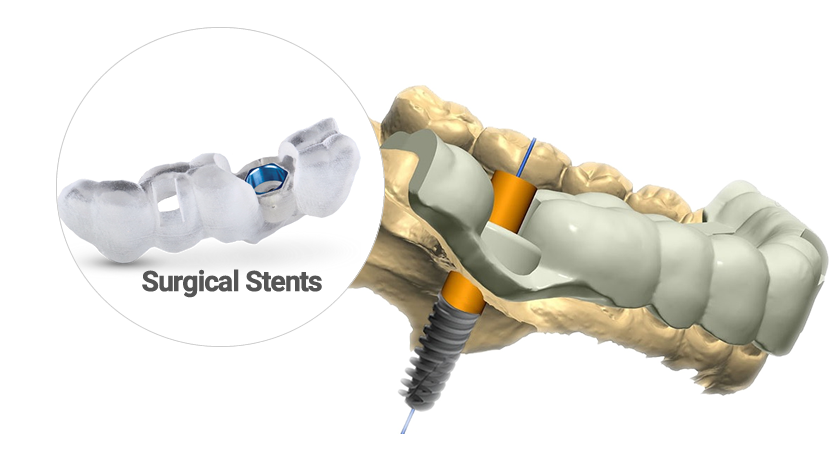
SURGICAL STENTS IN DENTAL IMPLANT SURGERY
A surgical stent, also known as a surgical guide or template, is a crucial tool used in dental implant surgery to ensure precision, accuracy, and optimal outcomes. It’s a custom-made device that fits over a patient’s teeth and gums, serving as a guide for the placement of dental implants. The stent is created based on detailed digital scans of the patient’s oral structures.
Why Surgical Stents are Used:
- Precision: Surgical stents provide a highly accurate guide for implant placement, ensuring that the implants are positioned precisely according to the treatment plan. This precision is crucial for the long-term success and stability of the implants.
- Minimized Trauma: The stent helps reduce the need for extensive tissue manipulation during surgery, which can lead to reduced trauma, faster healing, and decreased discomfort for the patient.
- Predictable Results: By using a surgical stent, the dentist can predict and plan the final position of the implants, resulting in more predictable aesthetic and functional outcomes.
- Ideal Angulation and Depth: The stent ensures that implants are placed at the correct angle and depth, optimizing the biomechanics of the implant-supported restoration.
- Time Efficiency: The use of a surgical stent can lead to shorter surgery times, as the precise positioning of implants is facilitated, reducing the need for adjustments during surgery.
- Minimized Infection Risk: With precise placement and reduced tissue manipulation, the risk of post-operative complications, such as infections, can be minimized.
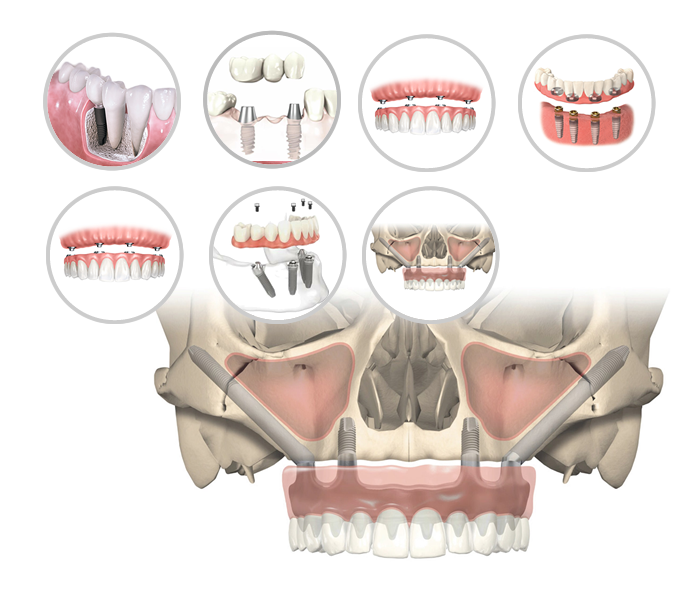
DENTAL IMPLANTS USAGE IN RESTORATION OF MISSING TEETH
-
- Dental implants can be used in various ways to restore missing teeth, depending on the specific needs of the patient. Here are the different ways dental implants are commonly used for tooth restoration:
- A single dental implant can be used to replace a single missing tooth. An implant is placed in the jawbone, and a custom-made crown is then attached to the implant abutment, creating a natural-looking and functioning replacement tooth.
- When multiple adjacent teeth are missing, an implant-supported bridge can be used. This involves placing dental implants at each end of the gap and attaching a bridge that spans the space. The bridge is secured to the implants, eliminating the need for support from adjacent natural teeth.
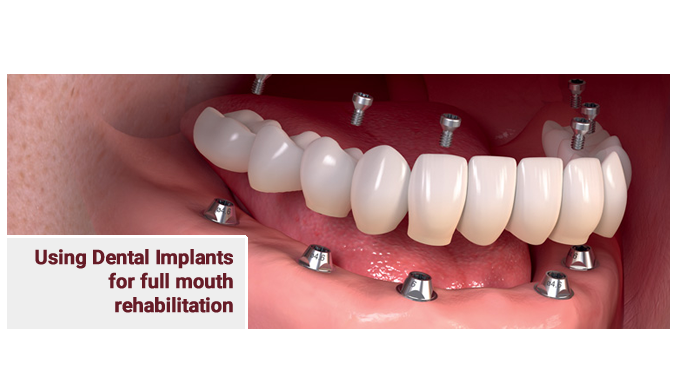
- Dental implants can support a full arch of teeth when all teeth in an arch are missing or need to be replaced. Implant-supported dentures offer better stability and retention compared to traditional removable dentures. These can be fixed or removable, depending on the patient’s preference and the treatment plan.
- This is a technique where a full arch of teeth is supported by only four (or six) strategically placed implants. This approach is often used in cases where the patient has significant bone loss, as it minimizes the need for extensive bone grafting procedures.
- Implant overdentures are removable dentures that are supported by dental implants. The implants provide stability to the dentures, preventing slippage and improving chewing efficiency. These can be secured by attachments or clips.
- For patients missing multiple teeth in different areas of the mouth, implant-supported removable partial dentures can be designed. These dentures are anchored to dental implants and provide better stability than traditional removable partial dentures.
- Hybrid dentures are a combination of fixed and removable prosthetics. They are securely attached to dental implants but can be removed by a dentist for maintenance. Hybrid dentures provide a good balance between the stability of fixed restorations and the ease of maintenance of removable dentures.
- In some cases, a tooth may need to be extracted due to damage or decay. Immediate implant placement involves removing the damaged tooth and placing an implant in the same session. This approach can help streamline the treatment process and reduce the overall treatment time.
Zygomatic implants are longer implants that are anchored into the cheekbone (zygomatic bone) when there’s insufficient bone in the upper jaw for traditional implant placement. They are used in cases of severe bone loss in the upper jaw.
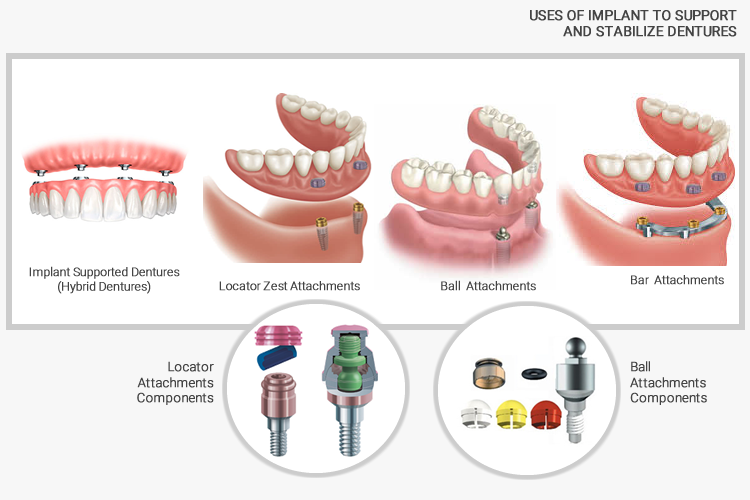
IMPLANTS SUPPORTED HYBRID DENTURES
Hybrid Dentures are Screw-Retained Dentures that are fixed implant solution for edentulous patients desiring a replacement for removable prostheses. Our specially trained technicians use our state-of-the-art scanning and CAD/CAM technology to design and manufacture a titanium framework. Acrylic and denture teeth are processed onto the milled titanium bar, providing a fixed prosthetic solution with a precise and comfortable fit.
- As treatment calls for the placement of traditional dental implants, patients are carefully evaluated to determine if they are candidates for hybrid dentures. Our goal is to conserve as much of your natural smile as possible. Our Lorton oral surgeon recommends hybrid dental implants for patients who are missing most if not all the teeth in an arch. Patients who have previously used dentures but are otherwise in good health are also excellent candidate for hybrid implant dentistry.
USES OF IMPLANTS TO SUPPORT DENTURES
A thin metal bar that follows the curve of your jaw is attached to two to five implants that have been placed in your jawbone. Clips or other types of attachments are fitted to the bar, the denture or both. The denture fits over the bar and is securely clipped into place by the attachments.
(stud-attachment dentures) — Each implant in the jawbone holds a metal attachment that fits into another attachment on the denture. In most cases, the attachments on the implants are ball-shaped (“male” attachments), and they fit into sockets (“female” attachments) on the denture. In some cases, the denture holds the male attachments and the implants hold the female ones.
Hybrid implant dentures consist of dentures that are fixed onto implants. These dentures use prosthetics to replace full rows of teeth. The dental implants support a titanium or gold bar that anchors a set of acrylic teeth in place. The bar is permanently fixed in one place which means your dentures won’t move around.
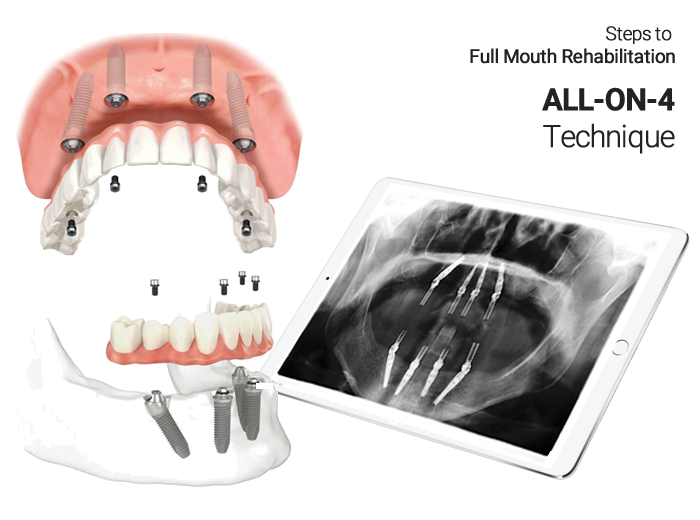
ALL-On-4 FULL MOUTH RECONSTRUCTION
The All-on-4 treatment concept is a prosthodontic procedure (i.e replacement of missing teeth) that provides a permanent, screw-retained, same-day replacement for the entire upper and / or lower set of teeth with a bridge or denture. The procedure is best for patients with significant tooth loss or decay and for people whose bone loss in the jaw area prevents them from getting conventionally oriented (vertical) dental implants. Often, tooth loss is accompanied by loss of the jaw bone which poses the problem of reconstruction of the jaw bone requiring bone grafting.
- All-on-Four technique takes advantage of the dense bone that remains in the front part of the jaws and by placing the two posterior implants on an angle to avoid the sinus cavities in the upper jaw and the nerve canal in the lower jaw.
- For the implementation to be successful a careful analysis of the bone structure needs to be made. The most ideal way to evaluate the bone is by a CBCT scan.
- The All-on-4 protocol is for at least four implants to be placed in a jaw.
- The implant is placed in front of the maxillary sinus in the upper jaw (maxilla) and in front of the mental nerve in the lower jaw (mandible).
- The head of the implant emerges in approximately the second premolar position. This will allow a molar tooth to be cantilevered posterior resulting in a denture or bridge with approximately 12 teeth.